Inline JavaScript
You can run JavaScript code directly within a CustomJS module in your Make.com scenario. If you want to manage and write complex JavaScript functions, the Execute Stored Function module in CustomJS lets you run them with dynamic parameters
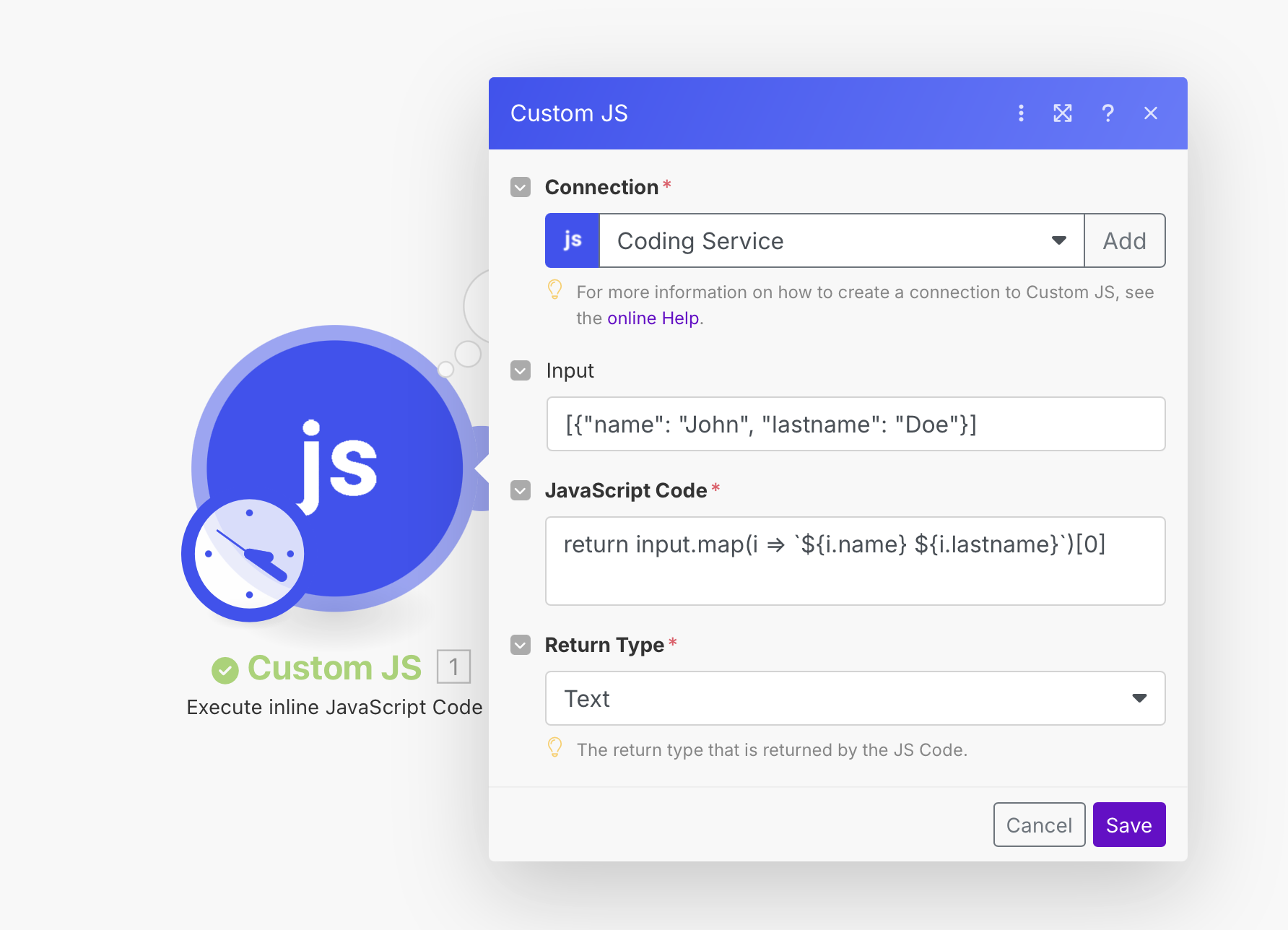
How it works
The customJS module consist of four fields: Connection, Input, JavaScript code and Return Type.
| Field | Description | How to use it |
|---|---|---|
| Connection | Links the module to the CustomJS service, enabling JavaScript execution. | Select or create a connection (e.g., Coding Service). Usually set up once and reused across scenarios. |
| Input | Data passed into the JavaScript code, available as the input object. | Enter plain text, arrays, or valid JSON strings. For Make collections, convert them with Transform to JSON first. |
| JavaScript Code | The script that will be executed by CustomJS. Must follow JavaScript syntax. | Ensure the code ends with a return statement so data is passed back to Make. |
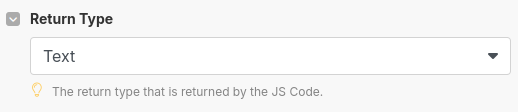
| Return Type | Defines the format of the data output back into Make. | Choose the appropriate type: Text, Object, Array, or Binary, depending on how the output will be used. |
Input variables
Inputs are accessed through the input object. For complex scenarios, you can:
- Pass JSON objects as input (must be valid JSON strings).
- Convert Make collections to JSON using the Transform to JSON module.
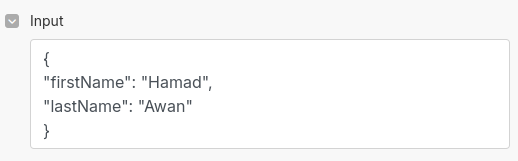
Working with Make collections
If you're passing a Make collection as input, use the Transform to JSON module to convert it before using it in your JS code.
Set the return type
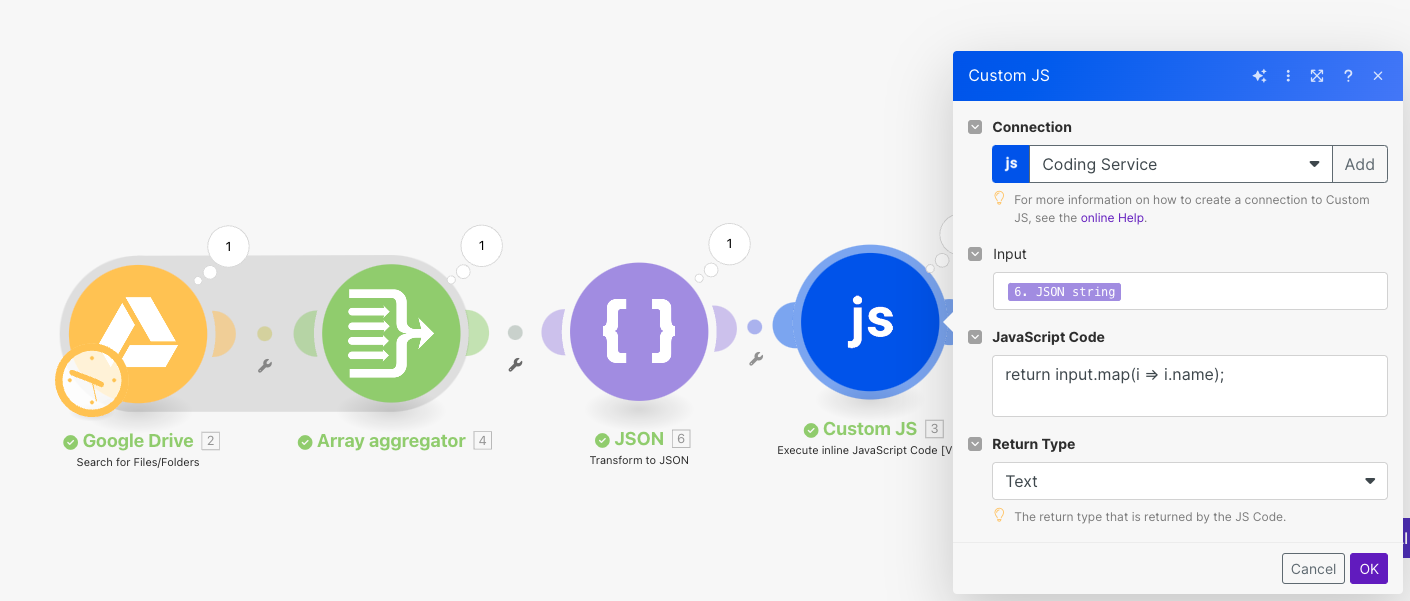
return Statement
In CustomJS, the JavaScript you write has to explicitly tell Make what value to send back. The only way to do that is with a return statement.
If you don’t include return, the code may run internally, but Make won’t receive any result, so the workflow won’t have any output to continue working with.
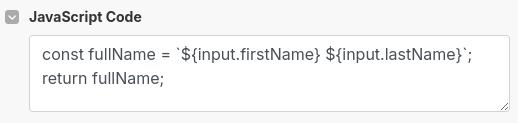
| Without Return | With Return | |
|---|---|---|
| Code | // Example (won't return a value to Make)
const fullName = `${input.name} ${input.lastname}`;
// No return statement below — Make receives nothing | // Example (returns a value to Make)
const fullName = `${input.name} ${input.lastname}`;
return fullName; |
| Result | Make receives no output. The next module has nothing to use, so the workflow may fail or produce empty values. | Make receives the string (e.g., "John Doe"). This value can now be used in subsequent modules. |
Return statement guidelines
Return early for error handling
Use early returns to stop execution when required input is missing or invalid. Returning immediately when something is wrong avoids running the rest of the code and makes debugging easier.
| Without early return | With early return | |
|---|---|---|
| Code | // Incorrect: runs even with missing input
const processedEmail = input.email.toLowerCase();
return { processedEmail };
| // Correct: return early if input is missing
if (!input.email) {
return { error: "Email is required" };
}
|
| Result | Code crashes if input.email is undefined.
The workflow may fail with an error. | Code stops gracefully when input.email is missing.
Make receives a clear error message instead of breaking. |
Return consistent data structures
Always return data in the same shape (e.g., object with predictable keys). This makes downstream modules easier to configure, since they know what to expect regardless of success or failure. Moreover, a predictable output format prevents “undefined property” errors and simplifies mapping in Make.
| Inconsistent | Consistent | |
|---|---|---|
| Code | // Incorrect: returns different structures
if (input.success) {
return input.data;
} else {
return "Processing failed";
}
| // Correct: always return the same shape
if (input.success) {
return {
status: "success",
data: input.data,
message: "Processing completed"
};
} else {
return {
status: "error",
data: null,
message: "Processing failed"
};
}
|
| Result | Downstream modules can’t predict the format. This causes mapping errors or undefined values. | Downstream modules always get a predictable object. This makes mapping and error handling reliable. |
Await async results before returning
When using asynchronous code (like fetch, database calls, or API requests), await the result and then return it. If you forget await or don’t return the resolved value, Make will just get a pending Promise, not usable data.
| Without await | With await | |
|---|---|---|
| Code | // Incorrect: returns a Promise, not data
return fetch(input.url).then(res => res.json());
| // Correct: resolve the Promise before returning
const response = await fetch(input.url);
const data = await response.json();
|
| Result | Make receives a Promise instead of usable data. The next module cannot work with unresolved Promises. | Make receives the actual data (JSON object with status and content). The next module can directly use this result. |
Remove inline comments
Inline comments usually work if you place them correctly with line breaks. However, misplaced comments can prevent the code from running as expected. Consider removing them if you have issues.
| Inline comments | Without inline comments | |
|---|---|---|
| With inline comments | // return full name
return input.firstName + " " + input.lastName;
|
return input.firstName + " " + input.lastName;
|
| Result | Make may not receive the intended output if the comment interrupts code execution. | Comments cannot interrupt code execution. |