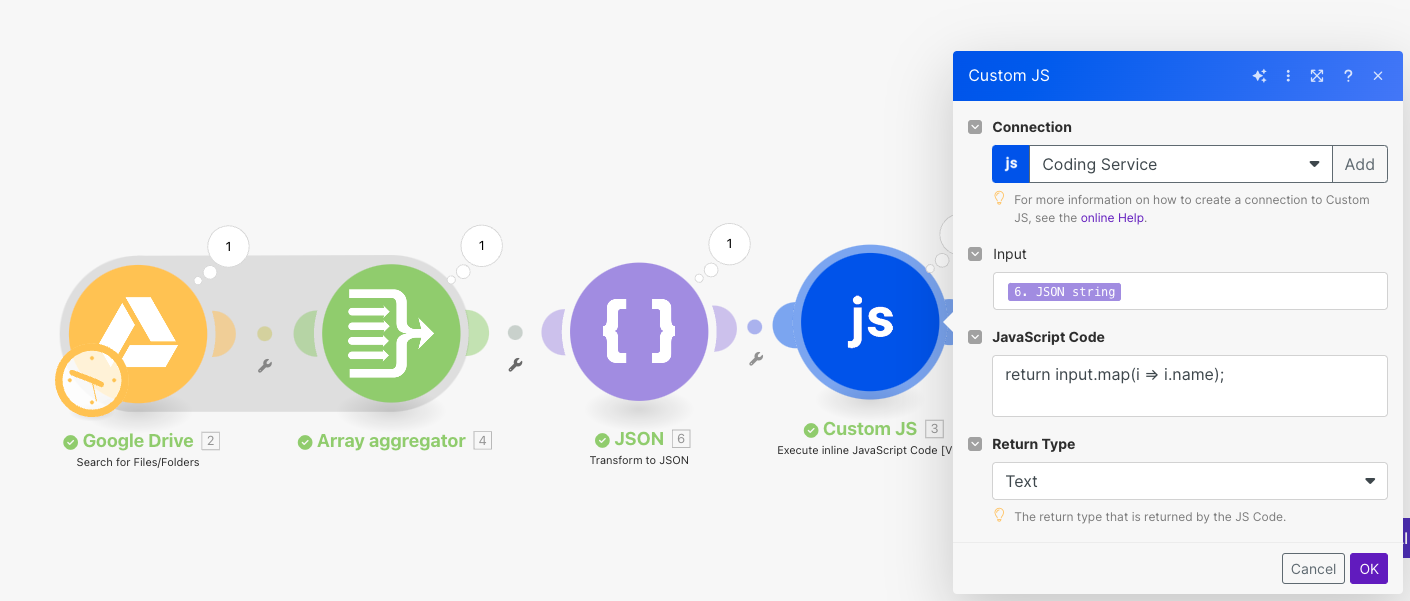
Make Collection to JSON
Make.com collections are arrays of data that flow between modules in your scenarios. If you want to use JSON structures from other Make modules, you must first convert the collection using the Transform a Make Collection to JSON module.